

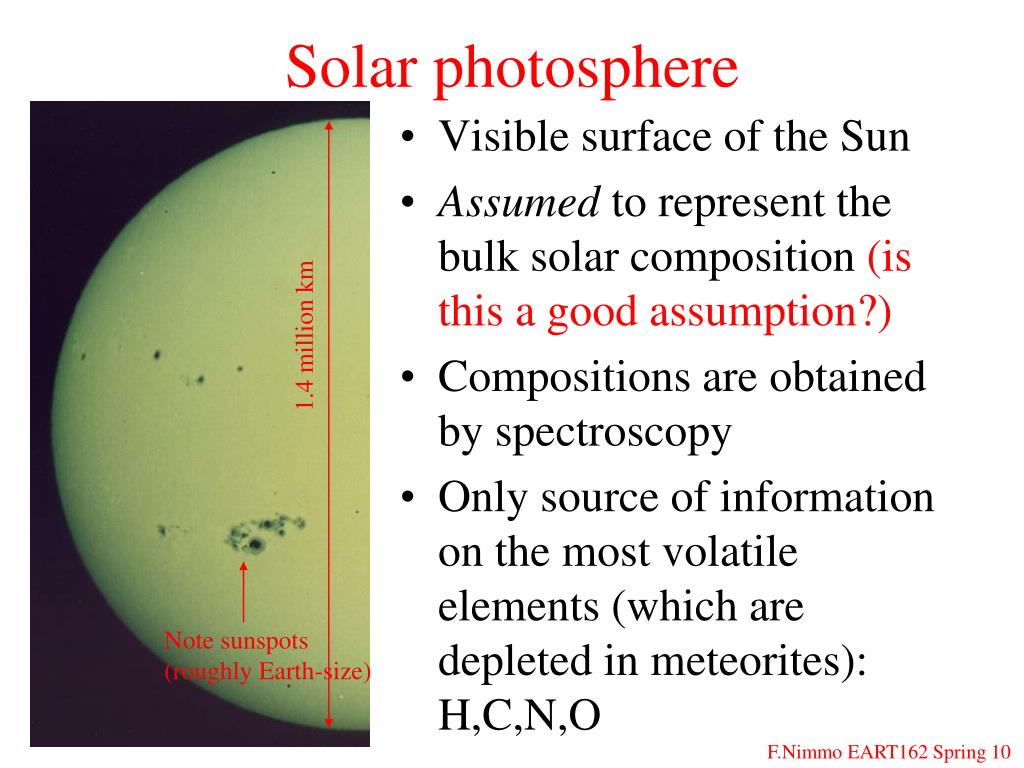
The surface of the sun is also called the "photosphere." This is because it is the layer of the sun where the light becomes free to travel away. The granular features here are about 1000 kilometers across in size.

This photograph of the sun's surface, taken edge-on, shows the 3-D nature of the granules.
Scharmer (ISP, RSAS) et al., Lockheed-Martin Solar & Astrophysics Lab The outer limit of the radiation zone is defined where the matter has become opaque to photons, and the energy is largely transported via convection.Ĭredit & Copyright: G. More and more, photons encounter atoms that have bound nuclei, which absorb the photons. This region of the sun's interior is called the radiation zone because the energy is mainly transported via radiation, or the movement of photons.Īs the photons make their way outward in the star, the plasma is also getting relatively cooler. Scientists calculate that it takes from a few hundred thousand to a few million years for a photon created in the core of the sun to reach the sun's surface, much of this time spent in the random walk through the radiation zone. This kind of motion is called a random walk. The photons can move about a centimeter before being absorbed and randomly emitted. In other words, the deep interior of the sun is transparent to photons. Since it is so hot, nuclei are ionized and relatively few collisions take place between free protons or electrons. As the photons make their way out of the core, they encounter matter particles and are absorbed and re-emitted.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
